第六周是讲虚拟化,其实虚拟化的架构什么的听着懵懵懂懂,但是这节课终于老师给了一道练习题,是关于计算的。因此,考试内容中可能会涉及到大量的计算,我很怀疑前面的计算也需要拿进来。所以回头得把前面的课题过一遍。
Virtualization: motivation and concept
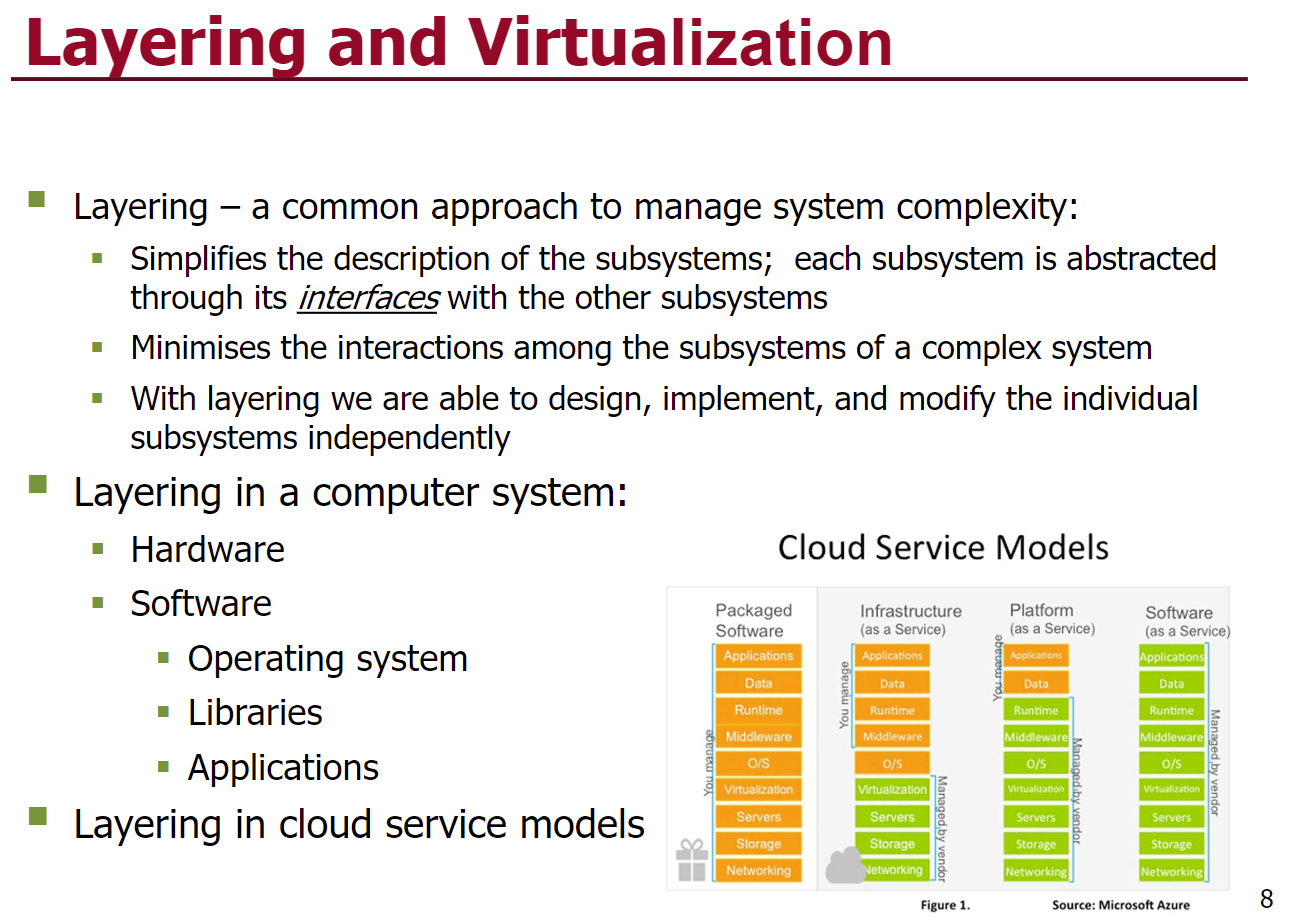
Layering and virtualization.
Dual mode execution and Processes
Virtual memory and page replacement
Virtual machine monitor.
Virtual machine.
x86 support for virtualization.
Full and paravirtualization.
Xen.
首先,简单介绍了抽象概念 用来描述计算机系统,包括处理器,内存,和沟通的link
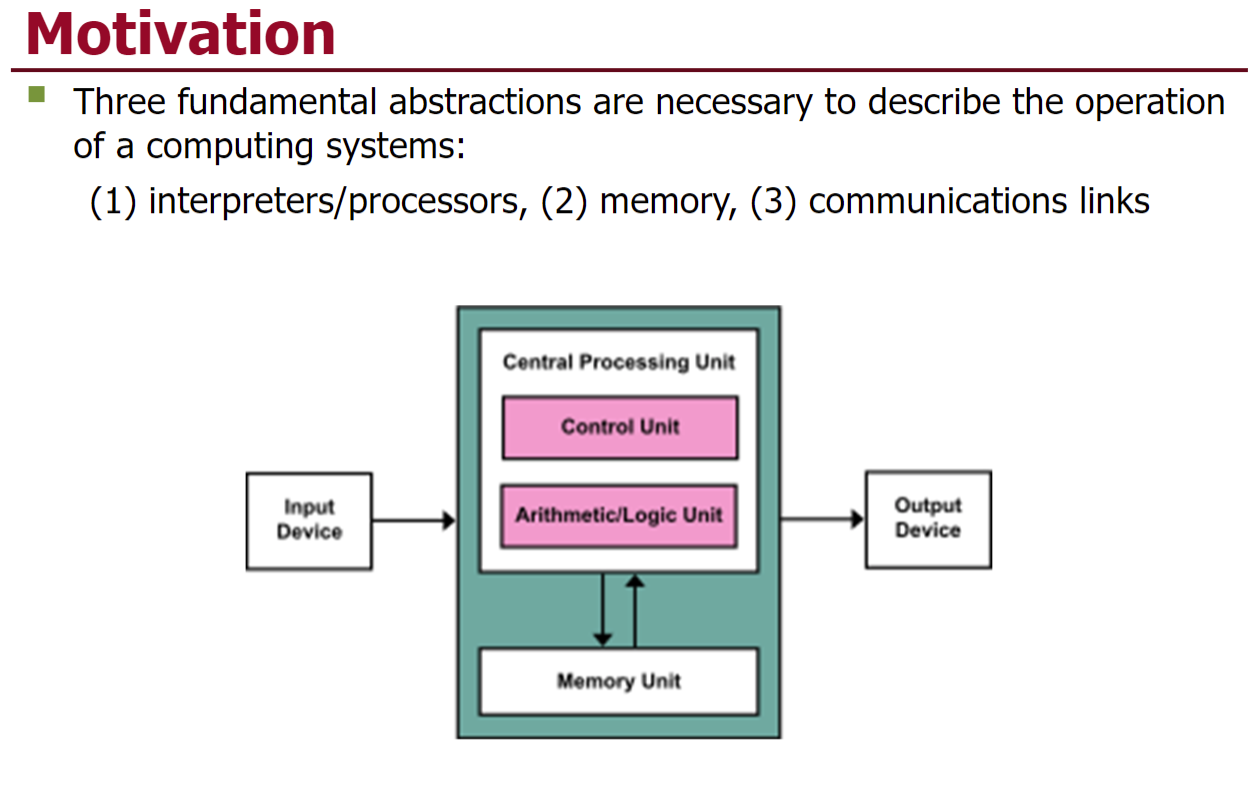
然后随着计算量,或者用户量的不断增加,慢慢的这种架构就面临着越来越大的挑战,例如如何处理峰值需求,heterogeneity 异质性。然后扯到了云计算的基础就是虚拟化。
Virtualization simulates the interface to a physical object by:虚拟化的几种方式
Multiplexing: creates multiple virtual objects from one instance of a physical object. Many virtual objects to one physical. Example - a processor is multiplexed among a number of processes or threads.
多路复用
Aggregation: creates one virtual object from multiple physical objects. One virtual object to many physical objects. Example - a number of physical disks are aggregated into a RAID disk.
聚合
Emulation: constructs a virtual object of a certain type from a different type of a physical object. Example - a physical disk emulates a Random Access Memory (RAM).
仿真
Multiplexing and emulation. Examples - virtual memory with paging multiplexes real memory and disk; a virtual address emulates a real address.
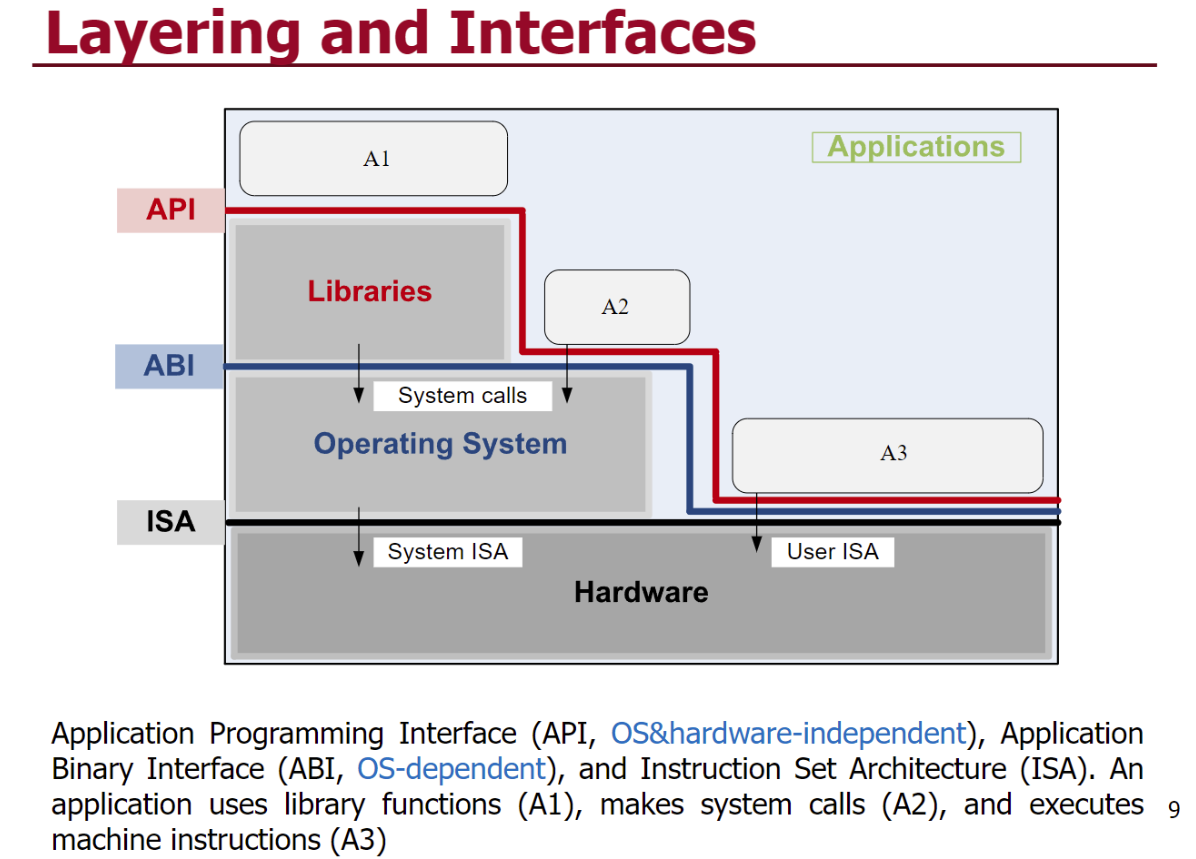
Instruction Set Architecture (ISA) – at the boundary between hardware and software.
Application Binary Interface (ABI) – allows the ensemble consisting of the application and the library modules to access the hardware; the ABI does not include privileged system instructions, instead it invokes system calls.
ABI is the projection of the computer system seen by the process.
Application Program Interface (API) - defines the set of instructions the hardware was designed to execute and gives the application access to the ISA; it includes high-level language (HLL) library calls which often invoke system calls
然后又开始听不懂了,全是底层架构
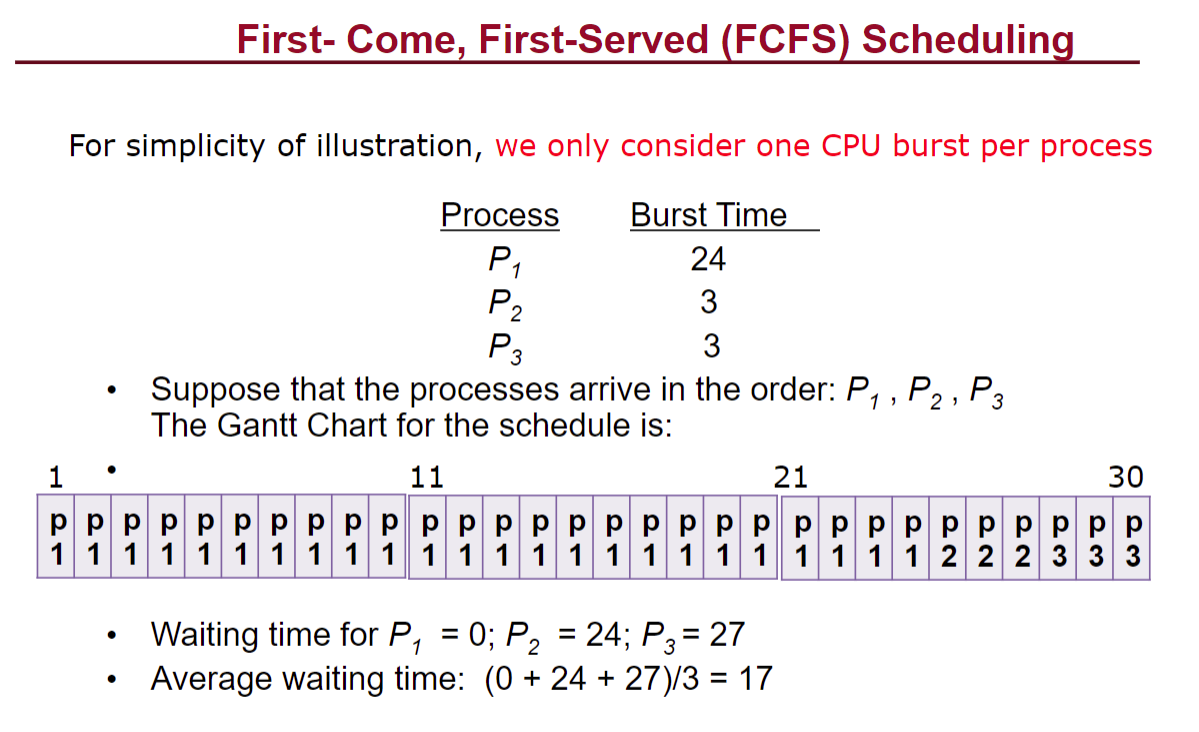

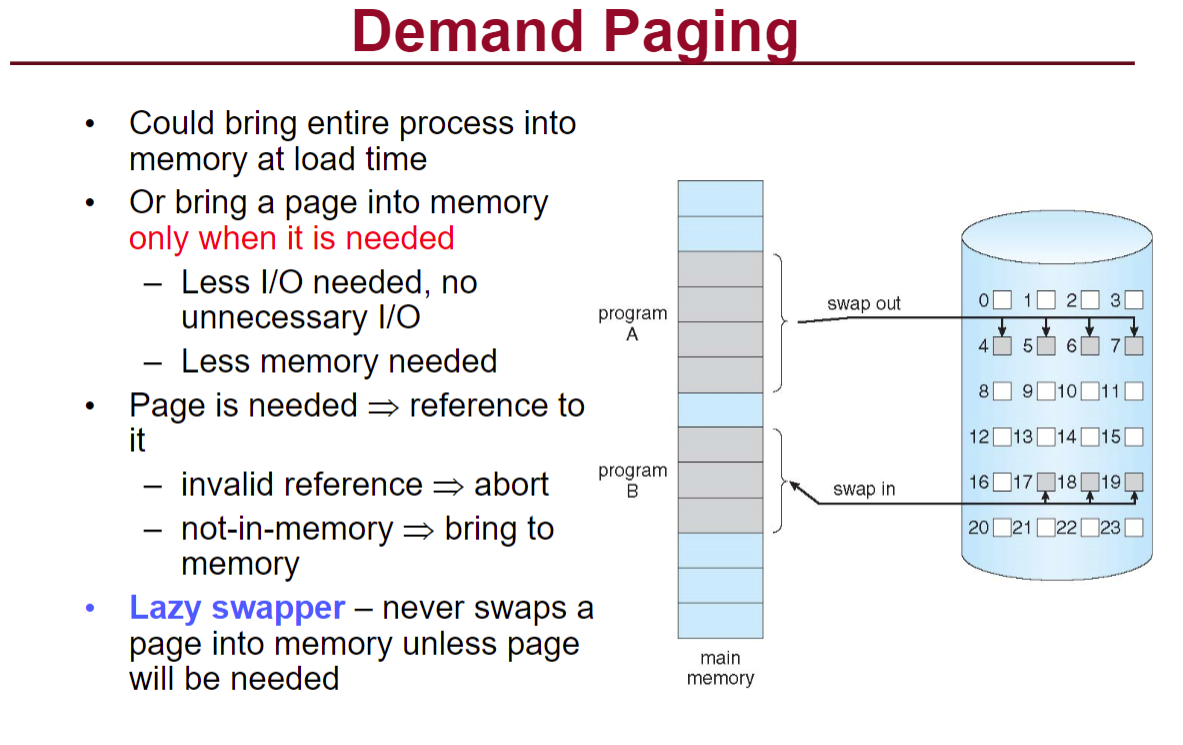
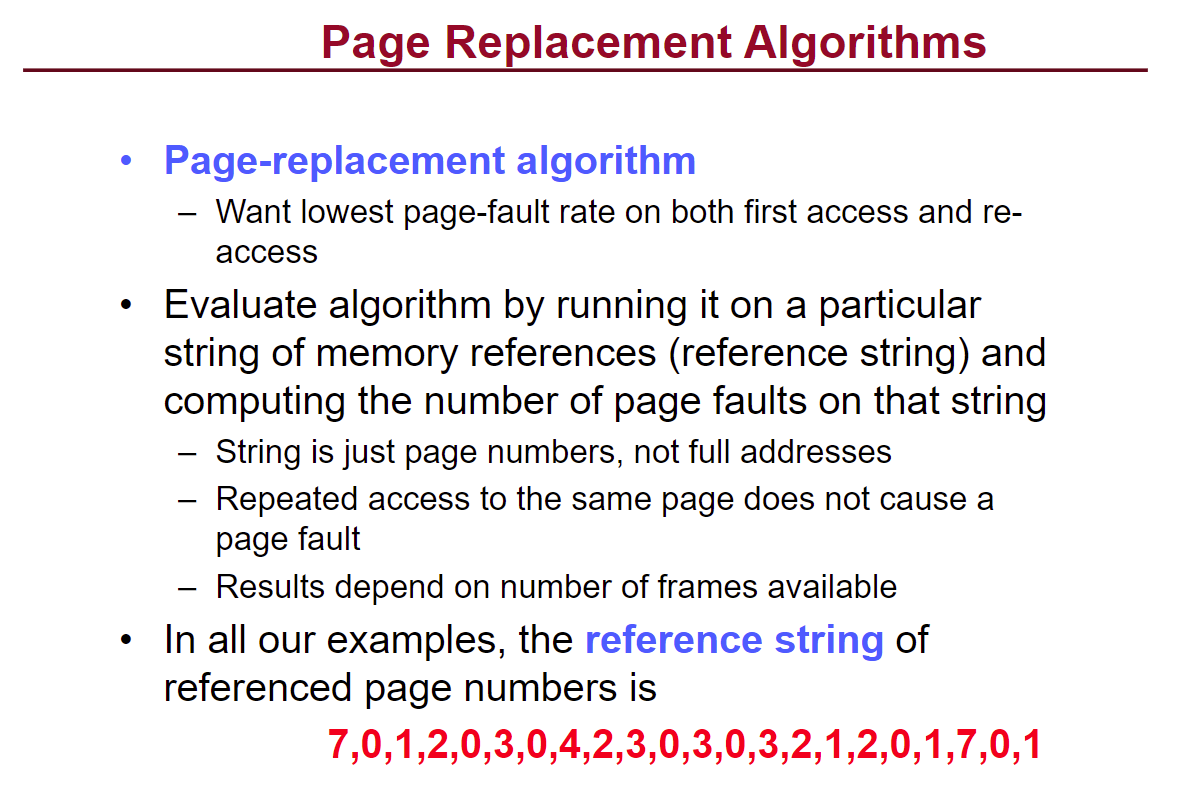
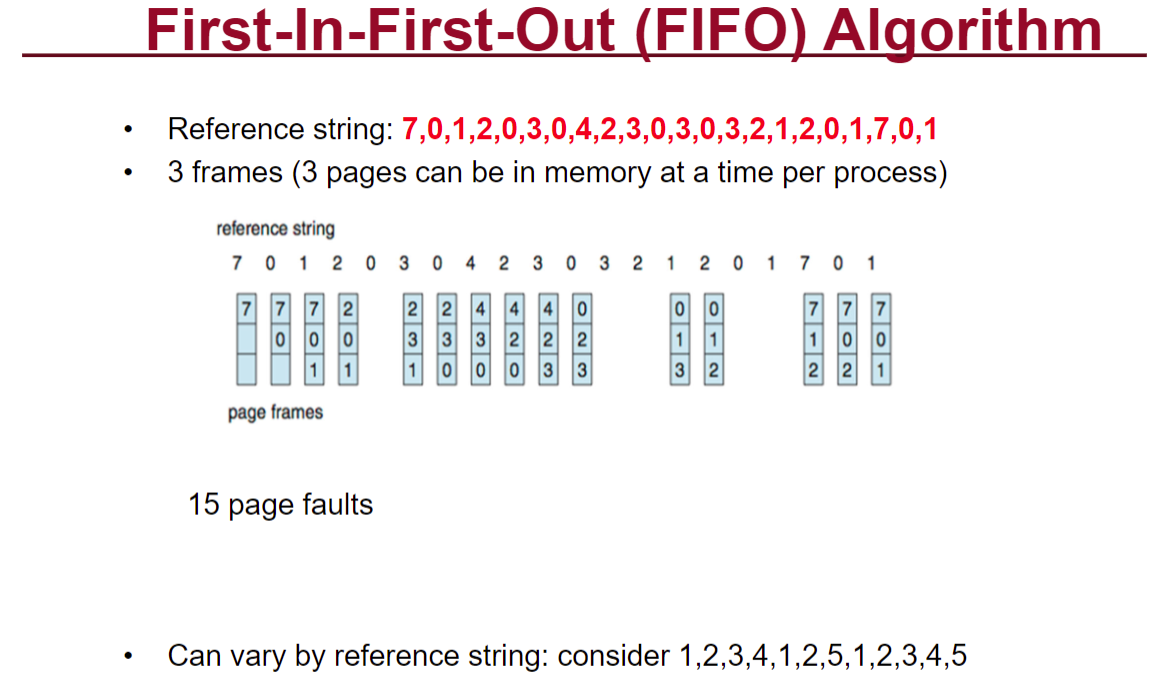
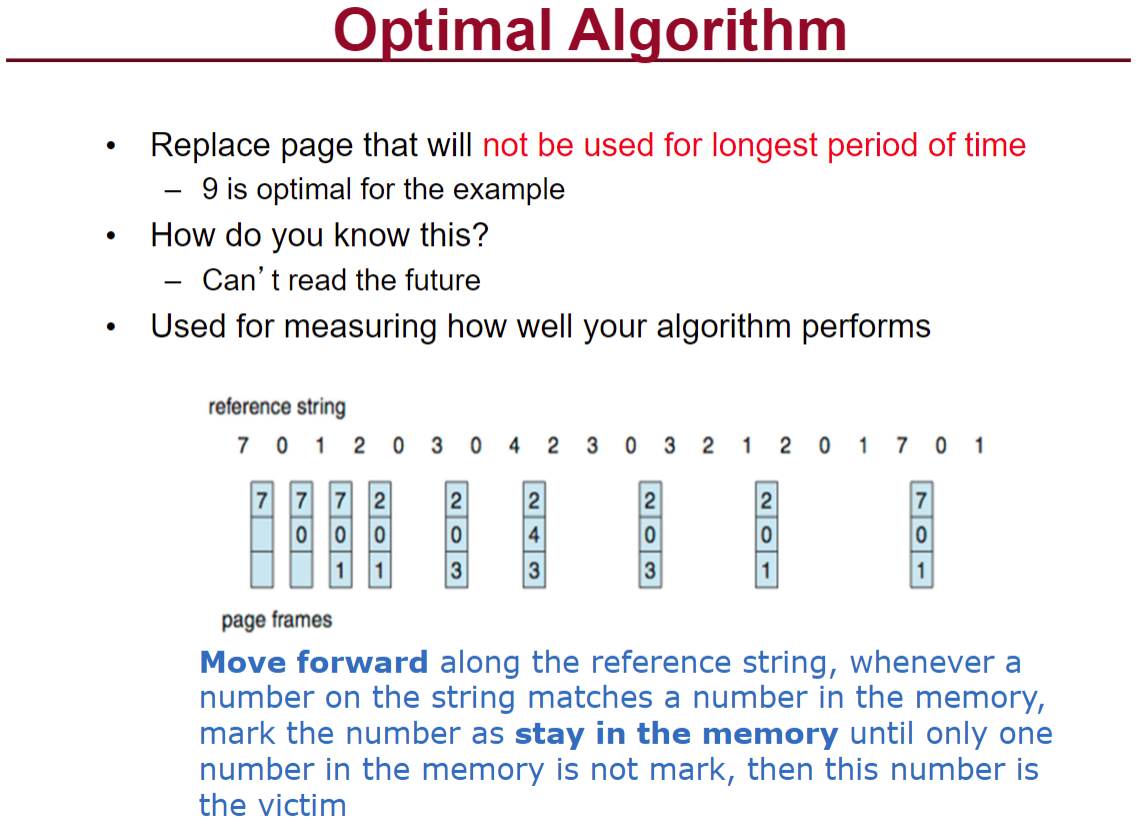
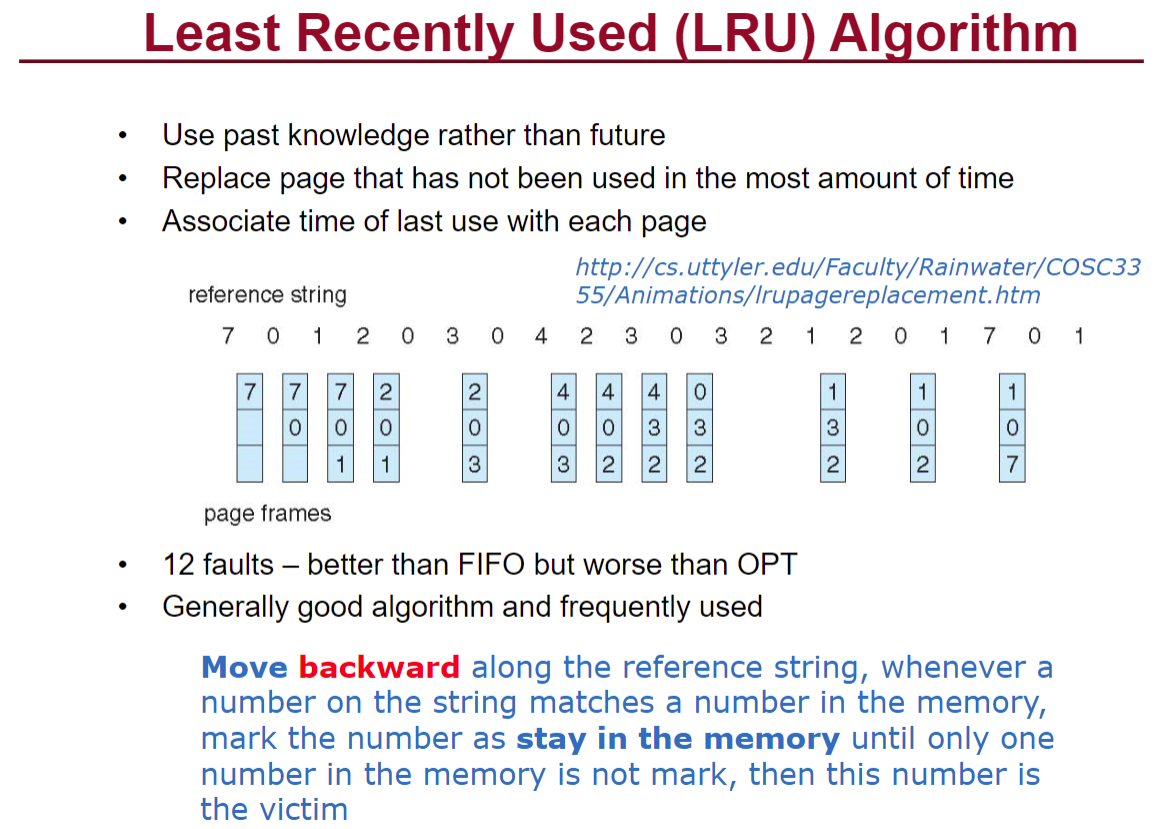
然后记住这个paging的计算
最后就是虚拟化的历史,一大堆东西
