Advanced Cybersecurity
First five weeks will be cybersecurity, while last 6 weeks will advanced digital forensics.
In the first three weeks, there will be guest lecture before the normal lecture. In this week, the guest introduction the real scenario in her forensics job and some basic thing about IoT.
Cybersecurity Introduction
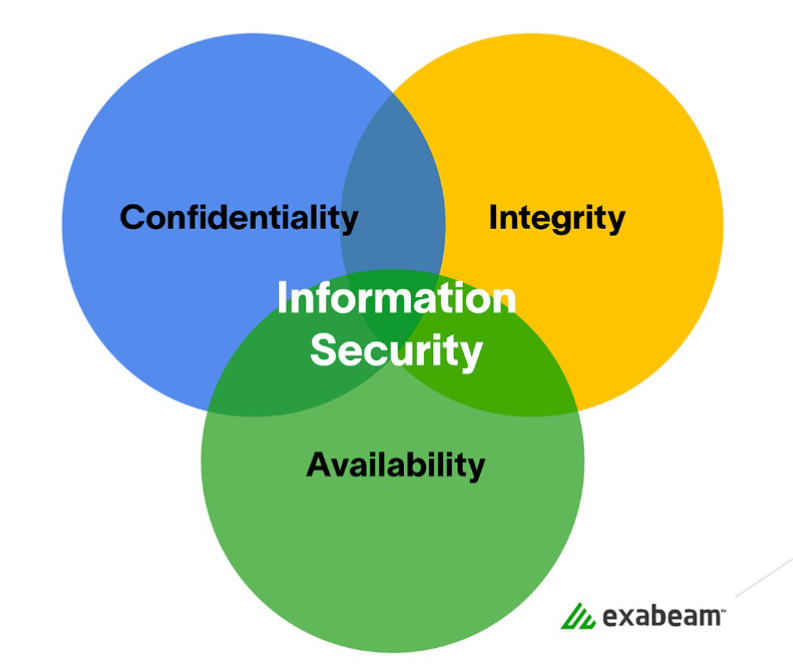
The five factors of cybersecurity is CIA or Confidentiality, Integrity, and Availability. Plus Authentication and Non-repudiation.
Nowadays, the amount of data producing is staggring.
Example: In London, if all the video recorded for only one day by security camera was stored in DVDs, and those DVD stacked on each other, the height would be taller than the Eiffel Tower.
Example: 5TB hard drive is fairly common, if a lecturer writing our the data in hexadecimal format. 4 bits for each alphanumeric character and each character 3cm wide. The total length will be 300 million kilometers. It is about earth to the sun and back.
5TB is 5,000,000,000,000 bytes multiplied by 2 to get hex is
10,000,000,000,000 hex characters.
10 quadrillion times 3cm = 30,000,000,000,000 cm divided by 100,000 = 300 million kilometres.
Also, if the lecturer write 1 character every second, it would take 051 thousand years to finish.Example: Edward Snowden stolen thousands of files to a USB stick, if those files were printed on A4 paper and stacked on top of each other, they would reach a height of over 7km.
BlockChain is not a computer security mechanism, it does not include 5 aspects of security. However, it could be used to allow for proof of provenance.
Cybersecurity in Business Cyber Risk
Cybercrime in business is often theft of data as 85% of a company's assets are now in digital form, but not just that.
Stealing the data
Modifying the data
Wiping the data
Due to the 85% of the world's infrastructure is controlled by computers. The 5th domain of warfare: land, sea, air, space, and cyber. Water, power, traffic lights, online payments, elections, etc., all of them becoming digitalised and therefore vulnerable to an attack from anywhere.
Cybersecurity in Business Resilience
Cyber resilience is built upon the existing security. It is bouncing back stronger and better protected than before an attack.
Budget
Tools
People
Processes
Cybersecurity in Business Regulation
The European Union worked for 5 years on theGDPR or general data protection regulation implemented on May 25th 2018.
Example, In 2018 British Airways was fined 200 million Euros for poor security controls on its web site affecting half a million customers’ details
Example, Facebook was fined $5 billion for its Cambridge Analytica data breach. Then FTC or US Federal Trade Commission let Facebook to do:
Document the implementation
Hire an independent privacy chief
Conduct risk assessments and evaluate the entire programme at least annually
Implement and thoroughly test safeguards
Implement training
Use outside experts for guidance
Cybersecurity in Business
RegulationFacebook vowed to spend US$3.7 billion on safety and security
Cybersecuriy in Business Cloud & IoT
The Average Cloud to On-Premises ratio in 2023 is 60:40 (USA)
The Pandemic has led to much more reliance on the Cloud
The data is the responsibility of the organisation
They must report an incident and bear most of the costs
IoT has led to more entrance & exit points in the network
Most IoT devices have no security built in
Most governments have no regulations for IoT
Many governments are now planning IoT regulations including:
Standards for encryption of data
Cybersecurity in Business Cyber Risk
A system is for creating, collecting, storing, processing and distribution of information. These systems can be internal systems developed in-house or purchased from a vendor.
[!NOTE]
The organisation is responsible for the data, whether on- premises or in the cloud, If the data is compromised, the organisation who owns the data must report the breach.
Endpoints are technology devices that allow communication back and forth within a network
Endpoints are the vulnerable point of a network system, including the cloud
Endpoints can be utilised to execute malware Desktops, laptops, IoT devices, cell phones
Risk may be inherited from the technology used. An IoT device inherits the risk built into all IoT devices. Then it is the risk inherent in the device. Next business processes can be interrupted by attack, DoS, Ransomware attack.
Cybersecurity in Business The digital link to the CIA triad
Cybersecurity in Business Cyber Exposure
Cybersecurity exposure is the potential financial loss for an organisation if the digital assets are compromised.
Example: SQL injection attack against Oracle version 8.0
Cybersecurity in Business Data Exfiltration
Data is stolen by insiders or external actors. Average cost of a single financial record is US$220. Average cost of a medical record is US$429
Example: Misconfigured systems, poor access controls
Data most at risk can be categorised as:
Customer Financial
Internal Employee
Intellectual Property
Cybersecurity in Business Other Loss
Intellectual property
Confidential corporate data
Product designs
Financial records of competition
All can lead to eroding the companies' competitive advantage
Cybersecurity in Business Business Interuption
Availability: authorised users cannot access systems or data.
Revenue
Recovery time
Business processes stop
Cybersecurity in Business Cyber Exposure Use Cases
Identify the riskiest assets to prevent data loss
Focus on the most significant assets
Determine the cyber insurance required
Mitigating Risk
Security Frameworks
Cybersecurity in Business COBIT 2019
ISACA Framework: Information Systems Audit & Control Association orovides a framework for governance of IT. There are 40 Governance and Management objectives. It includes technology and information processing guidelines and provides a performance management system
Summary
All contents are concepts that is very boring.
